What is chronic pelvic pain or CPPS?
Chronic pelvic pain syndrome (CPPS) in men is a chronic condition with an estimated 8-12% of men having characteristic symptoms of this syndrome at some point in their lives.
Pelvic pain syndrome usually involves pain in the pelvis, it can include pain in the lower back, legs, abdomen, penis (shaft, tip, urethra and base), testicles, perineum and prostate. It can also include urinary symptoms in the form of increased frequency of urination, urgency, nocturia (the need to urinate at night), dysuria (painful urination).
CPPS develops as part of chronic, non-bacterial prostatitis-IIIa, (inflammation in and around the prostate without the presence of bacterial infection). Symptoms can also worsen and cause an erectile dysfunction problem, leaving the patient with increased sensitivity in all of the above areas.
Chronic pelvic pain CPPS
Chronic pelvic pain syndrome (CPPS), also known as chronic nonbacterial prostatitis, is characterized by pain in the pelvic floor area. Symptoms can also affect the urinary tract, where there is frequent urination, painful urination, and the need to urinate during the night. The prostate plays a key role in this disorder where non-bacterial prostatitis develops, inflammation in and around the prostate, as well as adjacent organs, nerves and muscles. The syndrome is characterized by pelvic or perineal pain without evidence of urinary tract infection. Symptoms may wax and wane. The pain can range from mild to debilitating. Before your doctor can treat you for the pain of CPPS syndrome, all other possible diagnoses that may lead to similar symptoms must first be ruled out.

Treatment of CPPS
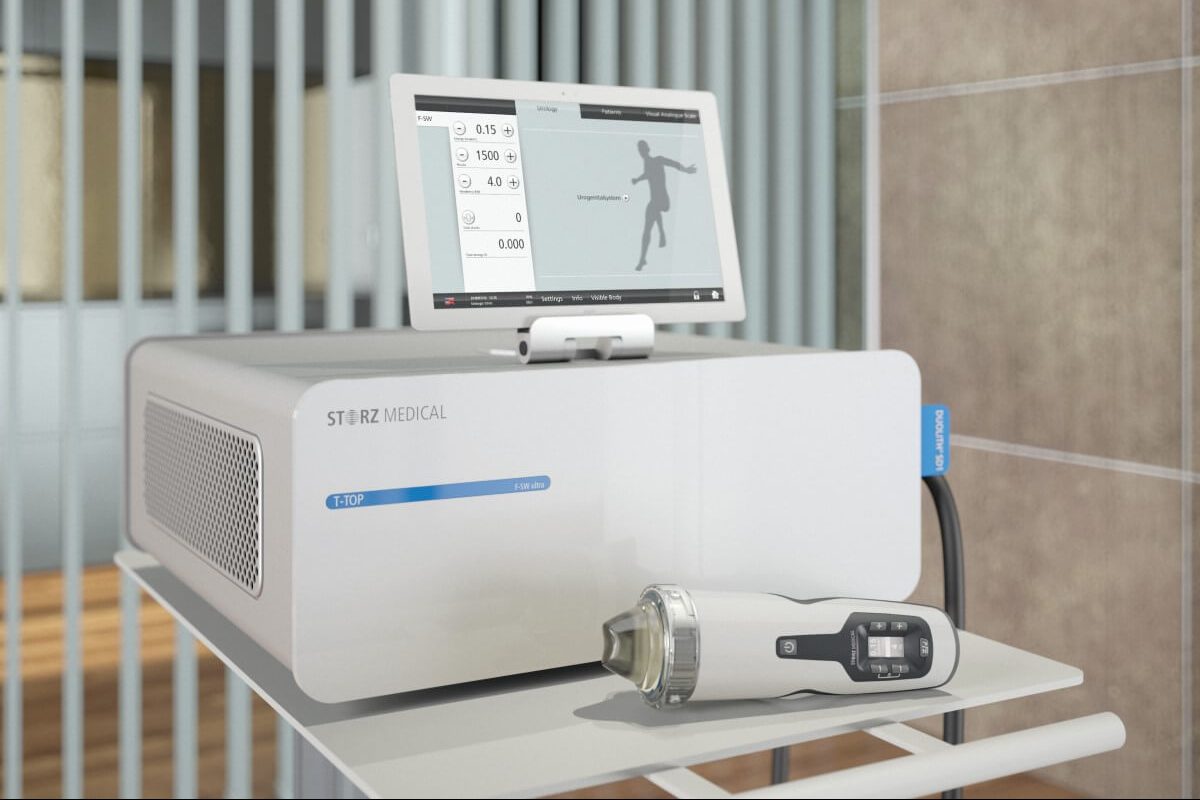
Extracorporeal shock wave therapy involves the application of shock waves to the perineum, prostate and pelvic floor. In a 2009 study, all patients showed a statistically significant improvement (compared to the placebo group) in terms of pain, painless and normal urination, as well as quality of life. A further study showed that ESWT is a safe and proven effective treatment for CPPS. The treatment takes between 15 and 20 minutes. On average, between four and six treatments are needed, depending on the severity and how the patient responds to treatment. Long-term effects of therapy cause cell membrane modification and functional changes. A number of cell signaling and biological activation processes are carried out, such as cell proliferation, angiogenesis, peripheral nerve regeneration, increased cell permeability and anti-inflammation. In our clinic, examinations and therapies are carried out by professor of urology Aleksandar Vuksanović, from the urology clinic of the KC of Serbia .
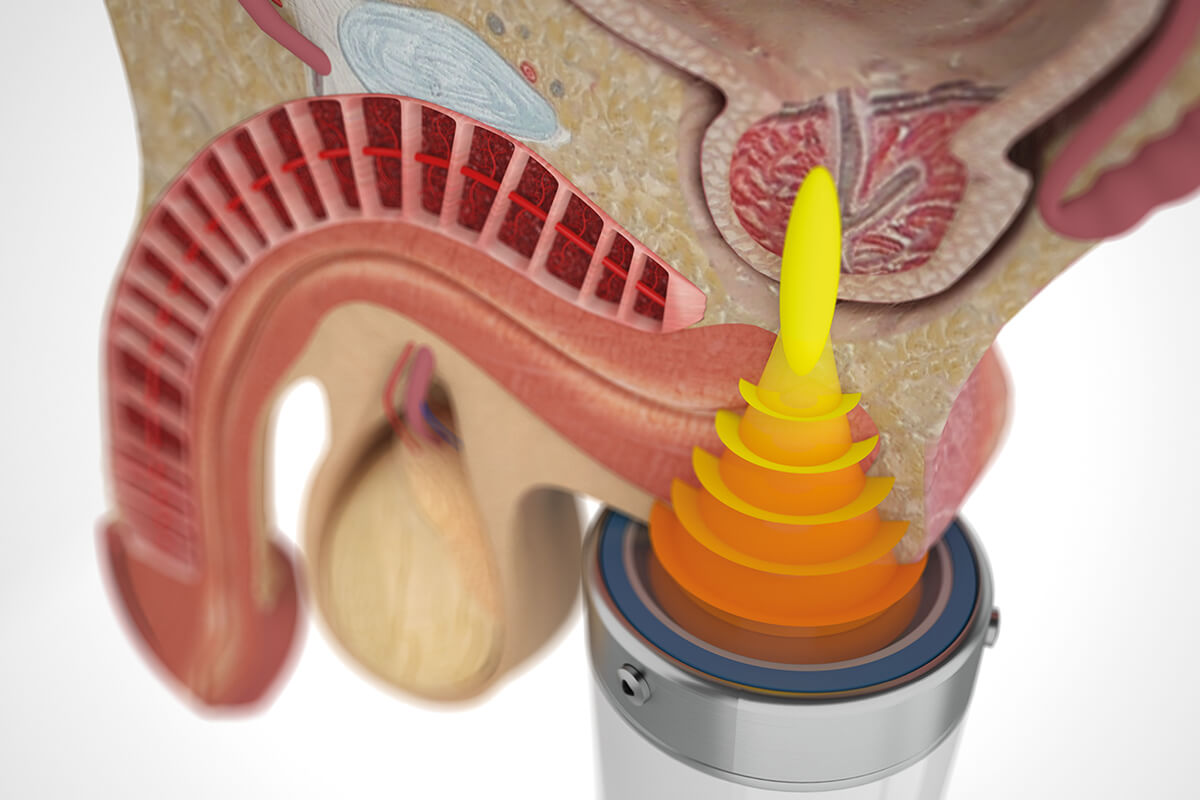
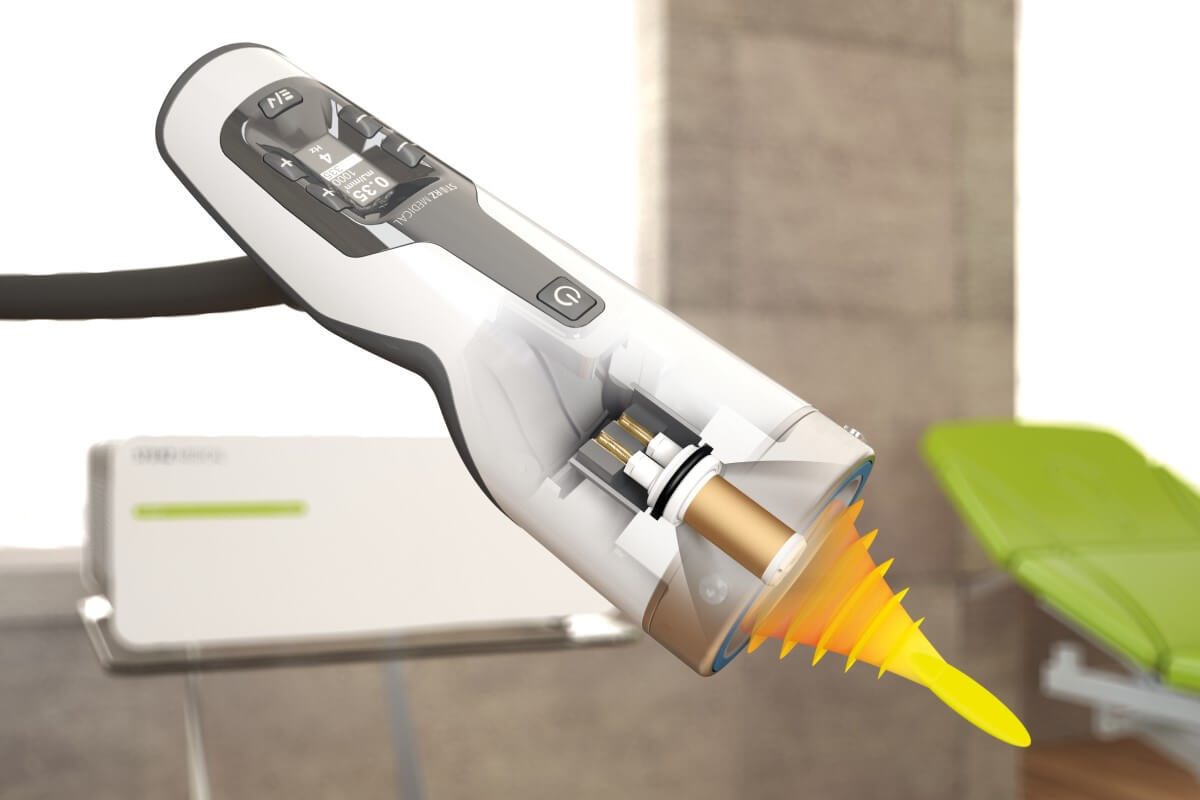
What are shock waves?
Since as early as 1980, shock waves have been successfully used in medicine to treat many orthopedic problems. Why is this procedure called "extracorporeal shock wave therapy" ESWT? The term "extracorporeal" in translation "extracorporeal" means "outside the body", where these shock waves are generated. With the device, we introduce waves into the body where they manifest their effect. ESWT, as a type of electropneumatic shock wave, is transformed into biochemical signals in a process called mechanotransduction, which can aim to hyperstimulate nociceptors and interrupt pain nerve impulses.
The main advantage of this method of treatment (shock wave treatment) is reflected in the fact that the therapy is risk-free, non-invasive, completely painless and without side effects.

